Uncategorized
30kW High-Power Laser Cutting: The Blade of Light in Modern Industry
Introduction to Laser Cutting Technology
Laser cutting is an advanced manufacturing process that uses a high-energy laser beam to cut materials with exceptional precision and speed. By focusing the beam on the surface of the workpiece, it generates intense heat—often reaching tens of thousands of degrees Celsius—rapidly melting, vaporizing, or ablating the material. With the help of high-pressure assist gas, the molten material is blown away, creating a narrow, clean kerf. Compared to traditional mechanical or thermal cutting methods, laser cutting is non-contact, highly accurate, and causes minimal thermal distortion. It is especially suitable for complex shapes and automated production. As laser technologies continue to advance, the deployment of high-power laser sources has become a key driver of industrial upgrading. Among them, 30kW-class ultra-high-power laser cutters are now essential tools for high-efficiency, heavy-duty metal processing.
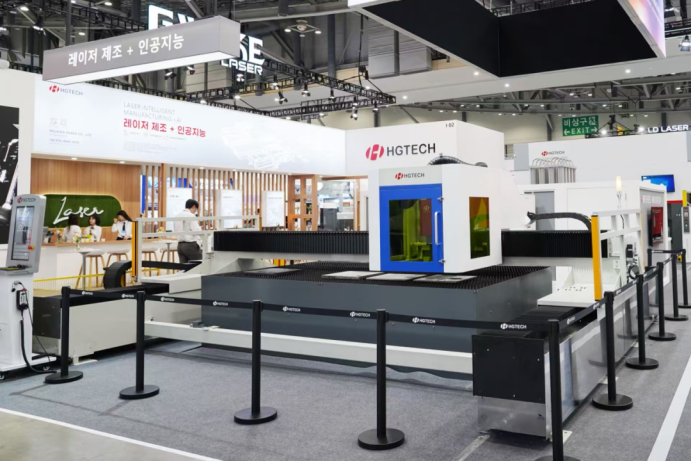

Technical Advantages and Industry Applications of 30kW Laser Cutting
The 30kW high-power laser cutting system represents the cutting edge of industrial laser technology, offering unparalleled capability in processing thick and high-strength materials. Its immense laser power enables clean, precise, and high-speed cutting of metal plates over 50mm thick—including carbon steel, stainless steel, and aluminum alloys—in a single pass. Cut edges are smooth and burr-free, with minimal heat-affected zones, ensuring excellent part quality and reducing the need for secondary processing.
One of the biggest advantages of 30kW laser systems lies in their stability and beam quality. Even under demanding conditions such as high-speed piercing or continuous long-cut paths, they maintain consistent performance and precision. Modern 30kW fiber laser cutters are also fully compatible with automated feeding systems, vision-based part recognition, and real-time process monitoring platforms. These integrations allow for intelligent, unmanned operations with higher throughput and lower labor costs. Smart control algorithms can auto-detect material type and thickness, adjust cutting parameters accordingly, and execute complex jobs with the push of a button.
This technology is rapidly being adopted in heavy industry sectors. In shipbuilding, for example, large-format structural steel plates require precise and efficient preparation for welding. Traditional oxy-fuel or plasma cutting is being replaced by high-power laser systems that deliver cleaner edges and tighter tolerances. In construction equipment and rail manufacturing, where complex geometries and high-strength alloys are common, the 30kW laser system handles customization and batch production with ease. In the renewable energy sector, where demand for wind tower components, battery enclosures, and hydrogen storage tanks is growing, the 30kW laser’s ability to process thick, large-format materials efficiently gives manufacturers a clear competitive edge. As digital transformation accelerates across the manufacturing landscape, this level of laser power is becoming indispensable to meeting the challenges of higher flexibility, faster delivery times, and lower operating costs.
Outlook: Smarter, Greener, More Efficient
Looking ahead, 30kW high-power laser cutting systems are evolving toward greater intelligence, sustainability, and efficiency. As part of the shift toward smart factories, these machines are increasingly integrated with AI-driven vision systems, machine learning algorithms, and adaptive process controls. Combined with Industrial IoT platforms, they enable real-time monitoring, remote diagnostics, and predictive maintenance—reducing downtime and enhancing operational visibility. Energy efficiency is also a focus: improved electro-optical conversion rates and more advanced cooling systems are helping lower the environmental footprint of high-power laser operations. In this new era of green and intelligent manufacturing, 30kW laser cutting is not just a productivity tool—it is a cornerstone technology for the next generation of industrial growth.