Projects
Application of Laser Cutting and Welding in Aerospace Manufacturing
Laser processing plays a key role in the aerospace field
The ability of laser processing to improve productivity and maintain low costs may play a crucial role in achieving this response in the aerospace industry. Laser processing – operations achieved through cutting, welding, shot peening, and drilling have become an indispensable part of aerospace manufacturing.

For example, lasers are used to manufacture flaps, wing fasteners, jet engine components, and seat components of aircraft wings, as well as to repair turbines, clean or remove paint from components, and prepare component surfaces for further processing. In recent years, laser additive manufacturing (AM) has become increasingly popular in the field of aerospace flight. In addition, the market hopes to improve the traceability of aerospace components, resulting in increasingly high requirements for laser marking.
High laser cutting accuracy
Laser cutting is a fast, cost-effective, and precise process that can be used to meet the stringent manufacturing requirements of the aerospace industry. Compared with traditional machining, laser cutting has high accuracy, less material waste, fast processing speed, low cost, and less equipment maintenance. In addition, due to its ability to make any necessary changes to the processing quickly and conveniently, it can maximize productivity.
Laser can be used to produce wing fastener parts, fixture parts, end effector parts, tooling parts, etc. It is also suitable for small components, such as grafting oil gaskets and titanium bleed pipe manifolds, as well as larger components, such as exhaust cones. It can process various aerospace materials, including aluminum, Hastelloy (nickel that has been alloyed with elements such as molybdenum and chromium), chromium nickel iron alloy, nickel titanium alloy, nickel titanium, stainless steel, tantalum, and titanium.
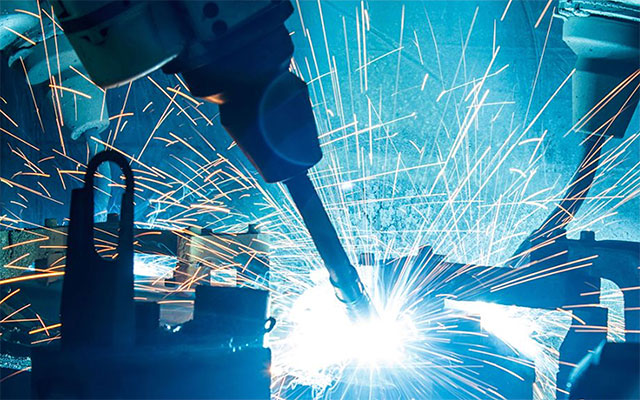
High laser welding efficiency
Laser welding is also used in the aerospace field as an alternative to traditional bonding methods, such as adhesive bonding and mechanical fastening. For example, the use of laser welding light aluminum alloy and carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) in aircraft manufacturing has received more and more attention, and has been used to replace riveting wherever possible. Laser swing welding and other technologies have also achieved success in fuel tank connection, improving connection efficiency and strength, reducing rework, and saving a lot of costs. Other successful welding cases in the aerospace field include: connecting the cast core of turbine blades to the cover plate; And creating new lightweight wing flaps to increase laminar flow control, minimize drag, and optimize fuel efficiency.
Compared with traditional methods, laser welding has the potential to save costs, reduce component weight and improve welding quality. At present, several manufacturers in the market have even begun to consider using laser welding to produce fuselage parts.