Projects
Introduction To Components Of Laser Sheet Cutting Machine
The workflow of laser sheet cutting machine
Laser cutting is the process of combining the laser emitted from a laser into a high-power density laser beam through an optical path system. With the assistance of a laser cutting system, the laser beam is precisely irradiated onto the surface of the workpiece, causing it to reach its melting or boiling point. At the same time, high-pressure gas coaxial with the beam blows away the melted or vaporized metal.
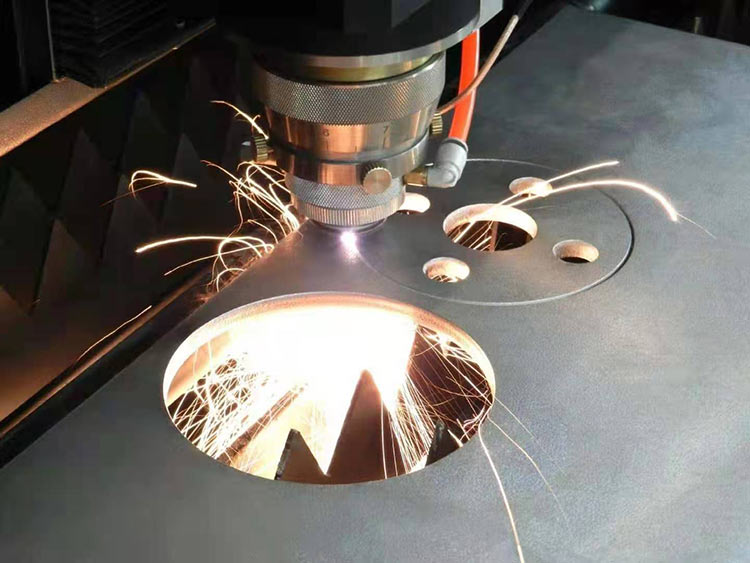

The functions of each part of the laser sheet cutting machine
1. Machine tool host part: The machine tool part of the laser cutting machine, which is the mechanical part that realizes the movement of the X, Y, and Z axes, including the cutting work platform. Used to place the cut workpiece and move it correctly and accurately according to the control process, usually driven by a servo motor.
2. Laser generator: a device that generates a laser light source.
3. External optical path: a refracting mirror used to guide the laser in the desired direction. To ensure that the beam path does not malfunction, all mirrors must be protected by protective covers and clean positive pressure protective gas should be introduced to protect the lenses from contamination.
4. CNC system: controls the machine tool to achieve X, Y, and Z axis movement, while also controlling the output power of the laser.
5. Stabilized power supply: connected between the laser, CNC machine tool, and power supply system. Mainly serves to prevent interference from external power grids.
6. Cutting head: mainly includes components such as cavity, focusing lens seat, focusing mirror, capacitive sensor, and auxiliary gas nozzle. The cutting head driving device is used to drive the cutting head to move along the Z-axis direction according to the program, and is composed of servo motors and transmission components such as screws or gears.
7. Operation console: used to control the entire cutting device’s working process.
8. Chiller unit: used to cool the laser generator. A laser is a device that converts electrical energy into light energy. For example, a CO2 gas laser typically has a conversion rate of 20%, and the remaining energy is converted into energy. Cooling water takes away excess heat to maintain the normal operation of the laser generator. The chiller unit also cools the external light path reflector and focusing mirror of the machine tool to ensure stable beam transmission quality and effectively prevent deformation or explosion caused by high lens temperature.
9. Gas cylinder: including the working medium gas cylinder and auxiliary gas cylinder of the laser cutting machine, used to supplement industrial gas for laser vibration and auxiliary gas for supplying cutting heads.
10. Air compressors and storage tanks: provide and store compressed air.
11. Air cooling dryer and filter: used to supply clean dry air to the laser generator and beam path to maintain the normal operation of the path and reflector.
12. Exhaust dust collector: Extract the smoke and dust generated during processing, and filter them to ensure that the exhaust gas emissions meet environmental protection standards.
Summary
The reason why using laser cutting equipment to cut sheet metal has the advantages of high accuracy, fast cutting, not limited to cutting pattern limitations, automatic layout saving materials, and smooth cutting is not only due to the role of the laser beam, but also the coordination of various components in the laser sheet material cutting machine.