Projects
Relay Laser Welding: Realize Fully Automatic Seal Welding
Relays are usually composed of electromagnets, contacts, springs and other components, among which contacts are the core components of relays, which directly affect the performance and life of relays. HGLASER will give you a comprehensive introduction to the advantages, difficulties, solutions and application of relay laser welding.
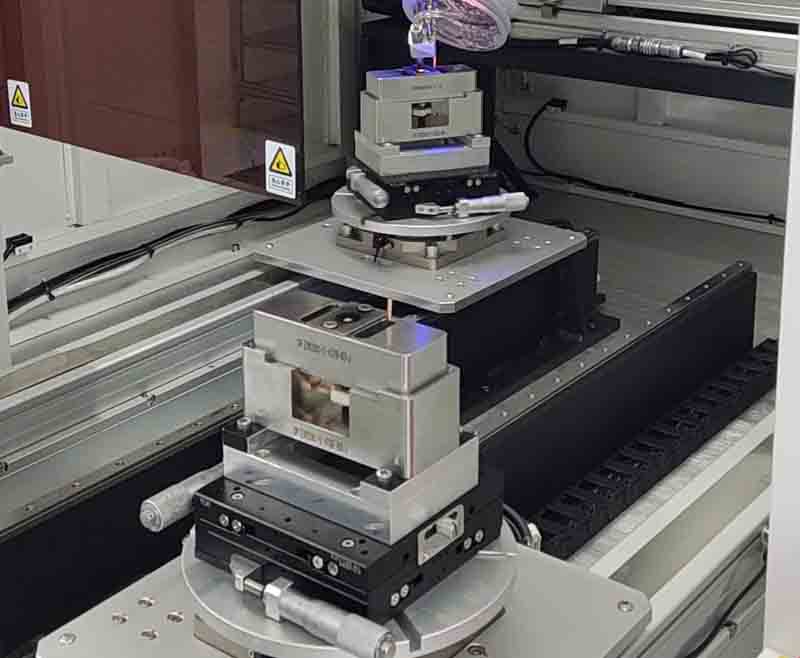

Advantages of relay laser welding
Compared with traditional welding methods, the advantages of relay laser welding are as follows:
1. Laser welding can achieve high-quality, high-precision, high-efficiency and low-cost welding, improving the performance and reliability of relays.
2. Laser welding can reduce the size and weight of relays, save materials and space, and improve the durability and aesthetics of relays.
3. Laser welding can weld different materials and refractory materials, expanding the design and application range of relays.
4. Laser welding can be carried out at room temperature or special conditions, reducing the impact on the environment and the harm to the operator.
5. Laser welding can achieve non-contact long-distance welding, providing great flexibility and automation. Laser welding can also achieve multi-beam simultaneous processing and multi-station processing, improving production efficiency and quality.
Difficulties and solutions for relays laser welding
Laser welding of relays may encounter some problems, such as cracks, pores, burn-through, etc. These problems will affect the performance and life of the relay, so some measures need to be taken to prevent and solve them. The following are some common problems and solutions:
Cracks
Cracks refer to fractures that occur in the center or edge of the weld. The main reasons for cracks are thermal stress and solid phase change stress during welding, as well as the chemical composition and solidification temperature range of the welding material.
In order to prevent the occurrence of cracks, the following measures can be taken:
1. Choose suitable welding materials to avoid elements that are prone to cracks, such as sulfur and phosphorus. For aluminum alloys, alloys with a narrow solidification temperature range, such as the 6000 series, can be selected.
2. Control welding parameters, such as laser power, speed, offset, line energy, etc., to make the weld shape reasonable and avoid stress concentration caused by excessive depth-to-width ratio or bulging in the middle.
3. Use preheating or post-heat treatment to reduce welding temperature gradients and residual stresses and improve weld structure and performance.
Porosity
Porosity refers to the voids that appear in the weld. The main reason for the occurrence of pores is the precipitation or inclusion of gas during welding.
To prevent the occurrence of pores, the following measures can be taken:
1. Clean the welding surface, remove impurities such as oil, rust, and scale, and avoid the introduction of moisture, hydrogen and other gases.
2. Use high-quality welding wire to avoid impurities or moisture.
3. Use sufficient protective gas, such as inert gas or mixed gas, to avoid the reaction of oxygen, nitrogen and other elements in the air with the weld.
4. Control laser parameters such as power, speed, and focus position to stabilize the keyhole and avoid gas inclusions caused by keyhole collapse or oscillation.
Burn-through
Burn-through refers to the penetration hole that appears in the weld. The main reason for burn-through is that the laser power is too large or the speed is too slow, resulting in a molten pool that is too deep or too wide.
To prevent the occurrence of burn-through, the following measures can be taken:
1. Select appropriate laser parameters, such as power, speed, offset, line energy, etc., to make the molten pool size reasonable and avoid being too deep or too wide.
2. Use appropriate filler metal or auxiliary arc to increase the support force and surface tension of the molten pool to prevent the molten pool from sagging or loss.
3. Use appropriate protective gas, such as inert gas or mixed gas, to prevent elements such as oxygen and nitrogen in the air from reacting with the weld, causing overheating or oxidation of the molten pool.
Application of relay laser welding
Relay is an electrical device used to control circuit switches and is widely used in various fields such as communications, automobiles, home appliances, industrial control, etc. Relay welding is an important process in the manufacturing process of relays, which directly affects the performance and reliability of relays. Laser welding is a process that uses a laser beam to heat parts to a molten state to achieve connection. The application of laser welding in relays mainly includes the following aspects:
1. Sealing of relay housing and base: The sealing of the relay housing and base is to ensure the vacuum or atmosphere inside the relay to prevent external moisture, dust, impurities, etc. from invading, affecting the contact life and triggering characteristics of the relay. You can use the waterless and oxygen-free glove box equipment of Laser to achieve high-quality, high-efficiency, and high-precision sealing welding, avoid deformation, cracks, pores and other defects caused by traditional welding methods, and improve the sealing performance and durability of the relay.
2. Spot welding of relay terminals, mounting ears, magnetic steel, magnetic isolation sheets and other parts: Relay terminals, mounting ears, magnetic steel, magnetic isolation sheets and other parts are important components of relays and need to be fixed or connected by spot welding. Laser welding can achieve precise spot welding of tiny and small parts, avoid defects such as overheating, burn-through, and melting caused by traditional welding methods, and improve the structural strength and stability of the relay.
3. Continuous spot welding of relay reeds and yokes: Relay reeds and yokes are the core parts of the relay, which determine the triggering time and triggering force of the relay. Laser welding can achieve continuous spot welding between reeds and yokes, avoid deformation, stress concentration, fracture and other defects caused by traditional welding methods, and improve the triggering performance and reliability of the relay.
Relay laser welding is an efficient and precise welding method that uses a high-energy-density laser beam as a heat source. It has the advantages of small welding heat-affected zone, small deformation after welding, high welding quality, and high degree of automation. Relay laser welding is widely used in relay sealing and connection, which guarantees the performance and life of the relay.